Cancer Data Science Pulse
NCI’s Cloud Resources Help Tame Today’s Data Windfall
Extraordinary improvements in data-generation technologies and plummeting costs over the past decade have led to a veritable explosion in the amount and variety of data sets available today. Leveraging these data to probe the biology of cancer presents unprecedented opportunities to fuel scientific breakthroughs in cancer research.
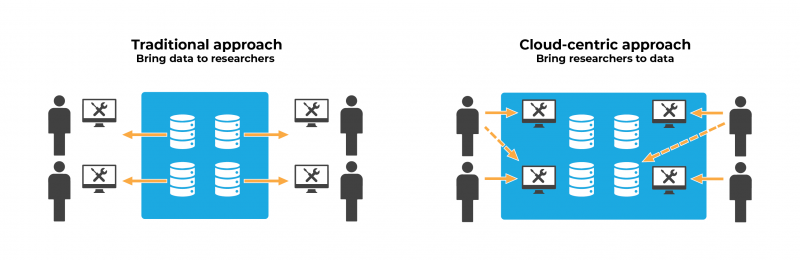
Yet this golden age of data generation also creates considerable challenges, as data sets stretch the limitations of the traditional data-sharing model. Until now, data were siloed in separate repositories or stored on each researcher’s desktop. This meant that data had to be downloaded to be useful. Unfortunately, as data sets grow ever larger, transfer times, computing power requirements, and data-management burdens have grown exponentially, putting researchers, particularly those at organizations without robust data infrastructures, at a disadvantage.
Many government agencies are working to solve these issues. Their goal is to make these data sets available on publicly accessible cloud platforms, along with powerful and highly scalable computing resources.
Any researcher with appropriate credentials can access and analyze data in the cloud without ever having to transfer a single byte of information. Researchers can tap into as much computing power as they need and break free of the infrastructure constraints imposed by their individual institutions. Through the cloud, researchers can federate multiple data sets, representing a rich tapestry of biological tissues and cellular states, and perform multi-omic analyses that have the potential to generate novel insights. Moreover, they can work collaboratively, sharing data, tools, and knowledge across institutional and international borders.
Introducing the NCI Cloud Resources
To truly advance data sharing and analysis, this cloud-based model needs resources that can be used by people with a wide variety of skills, and not just those with a background in computing and engineering.
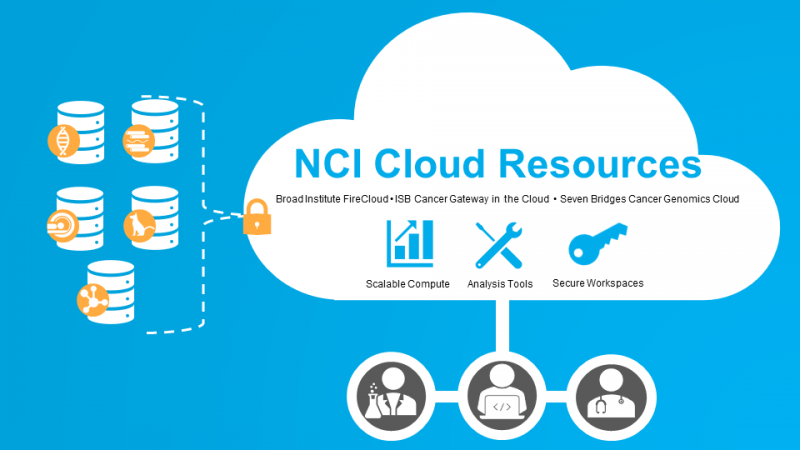
NCI’s Cancer Research Data Commons (CRDC) aims to address this need through cloud-based, intuitive interfaces offered by three NCI Cloud Resources: the Cancer Genomics Cloud, powered by Seven Bridges; the Broad Institute’s Firecloud, powered by Terra; and the ISB Cancer Gateway in the Cloud.
Through the CRDC, researchers have the data and computational power they need to better understand how cancer develops, how it progresses, and how it might be more effectively treated.
Each Cloud Resource is an independent platform built on top of one or more commercial clouds such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud. Each provides a unique combination of built-in tools and interfaces designed to empower researchers with all levels of experience, from bench scientists to bioinformaticians.
Working alongside the CRDC data repositories, the Cloud Resources enable researchers to access and analyze a deep catalog of data sets amounting to more than 3 petabytes of data, including those from The Cancer Genome Atlas Program (TCGA), The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA), and the Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC). Researchers also can bring their data to the cloud, analyze their findings in combination with other CRDC-hosted data sets, and leverage a variety of fully compatible data sources contributed by other organizations.
Acting as the analytical "powerhouse" of the CRDC, the Cloud Resources enable researchers to analyze data in a variety of ways, from running compute-intensive automated workflows on massive amounts of data, to exploring, visualizing, and analyzing data with popular data science and bioinformatics applications, such as Jupyter Notebooks, Rstudio, and Galaxy.
We invite you to take advantage of a treasure trove of community-contributed workflows and notebooks or bring your workflows into the system and share code and tools with collaborators.
The Real Impact of NCI Cloud Resources
There is a lot more to say about the Cloud Resources than we can cover in a single blog post. Rather than post a laundry list of features, we will be highlighting the core strengths of each of the Cloud Resources through a series of additional blog posts. Each blog will focus on a single platform and include real-world success stories of cancer researchers and computational scientists using the Cloud Resources.
In the meantime, please visit the Cloud Resources on the CRDC website for more details:
Leave a Reply
Categories
- Data Sharing (66)
- Informatics Tools (42)
- Training (40)
- Precision Medicine (36)
- Data Standards (36)
- Genomics (36)
- Data Commons (34)
- Data Sets (27)
- Machine Learning (25)
- Artificial Intelligence (25)
- Seminar Series (22)
- Leadership Updates (14)
- Imaging (13)
- Policy (10)
- High-Performance Computing (HPC) (9)
- Jobs & Fellowships (7)
- Semantics (6)
- Funding (6)
- Proteomics (5)
- Information Technology (4)
- Awards & Recognition (3)
- Publications (2)
- Request for Information (2)
- Childhood Cancer Data Initiative (1)

Yoshio Hayama on July 23, 2021 at 11:52 a.m.
I will study harder from data and dater.
Thank you again to all.