Cancer Data Science Pulse
For the Love of … Data! Drs. Kibbe and Almeida Discuss How Data Help Reveal Our Natural World
We’re continuing the celebration marking NCI’s 50th anniversary and recognizing the Power of Data, by asking NCI and CBIIT staff what data means to them and to the field of cancer research. In this post, we feature former NCI Deputy Director and CBIIT Director, Warren Kibbe, Ph.D. Dr. Kibbe is currently Vice Chair, Department of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics, and chief data officer at the Duke Cancer Institute. He also continues to support NCI, as a researcher, by serving on numerous advisory panels, and through the Childhood Cancer Data Initiative. Also featured is Jonas Almeida, Ph.D., chief data scientist and senior investigator within NCI’s Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics. Look for more perspectives on the power of data in the next blog!
What made you fall in love with data?
Warren: I’m not sure I can point to any one thing. For me it is similar to my love of science. There is a power in the scientific method to uncover the nature of our world, our universe, and ourselves. And for me, the scientific questions I am most interested in all revolve around the nature of living things and, of course, understanding the nature of cancer and how to reduce our risk, detect it earlier, identify the proper therapy, develop new therapies, and optimize our quality of life during survivorship. Answers to all of these questions need data!
Jonas: I share a similar view of using science to know more about our natural world. For me, this started when I was very young. I grew up in Angola in a place where animals appeared to want to “tell you stories.” In fact, I was told as a child that the only reason the animals didn’t actually talk was because “I didn’t listen.” I was particularly intrigued by an ant colony where all sorts of dramatic things occurred throughout the day. Yet sometimes, the ants were nowhere to be found. I had recently learned to write my numbers (this was a long time ago) and decided that every hour I would count how many ants walked across a given path. To my huge surprise, their wanderings kept a schedule, and I could trust my notes to tell me when and where to find them. I will never forget how surprised I was at that discovery. And many years later, when told in school that biology was too complex to be reproducible, I knew that wasn’t true. It can be solved through science using data!
What do you think has been the single greatest accomplishment in data science over the past 50 years of cancer research?
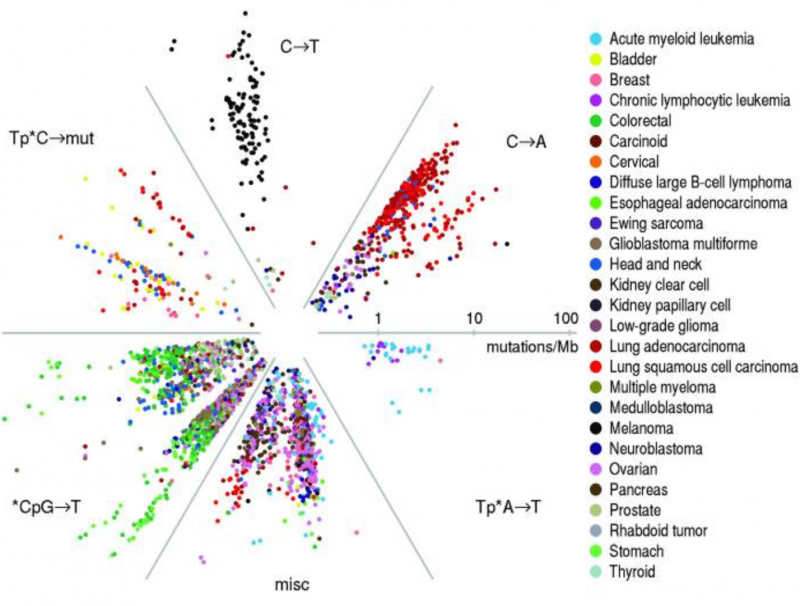
Warren: You’re right that data science’s roots extend back quite some time. Although Ada Lovelace is sometimes called the first computer scientist, she was also a data scientist and she lived in the early 1800s. Some 50 years later, Florence Nightingale used powerful data visualization techniques and infographics to explain the causes of mortality resulting from poor medical practices during a military campaign. That was more than 150 years ago! Moving into the last 50 years, there are so many advances to point to, it is hard to pick out just one thing. What I particularly like are combinations of elegant experiments and elegant data, with elegant visualizations that make really large datasets easily understandable. Like Manhattan plots for understanding GWAS data and the associations of specific point mutations with aggressive disease. Or the plot of mutation frequency across many cancers like The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) analysis published in 2013. (See figure.)
Jonas: I also think that TCGA was a very significant advance. Before TCGA we had to scramble to assemble bits and pieces of data on the many biological processes associated with the development of tumors. With TCGA, we have a collection of data with all those pieces—for the same individual, for tens of thousands of volunteers. Thanks to this data we are able to help so many people with so many different types of tumors.
As NCI embarks on the next 50 years, can you offer any practical tips or advice that should be considered?
Warren: Good data, good models, good experiments—all go hand in hand. That is true regardless of the area of research. Well-designed experiments that generate great data can be incredibly explanatory. And new techniques, new technologies, new analytic methods can change the types of questions we can ask, the quality of the data we can generate, and the biology we can explore. We need to always reassess and re-evaluate. The future is now! I hope that within another 50 years we’ll have better ways of preventing cancer, detecting it earlier, and treating it much more effectively. Ultimately, cancer will no longer be listed as a “leading cause of death” by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Jonas: We often apply quantitative methods, mathematical and computational alike, to a particular research endeavor that initially were developed for use in other disciplines. Fortunately, with the ubiquity of the Cloud and web computing, we’re increasingly able to reconfigure computational labs on the fly. I think we need to try and remove as many obstacles as possible to promote more computational reusability, such as the FAIR principles (that is, data are findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable). I think we should take them seriously and, in all cases, avoid the short-minded expediency of data silos and closed source applications.
Categories
- Data Sharing (66)
- Informatics Tools (42)
- Training (40)
- Precision Medicine (36)
- Data Standards (36)
- Genomics (36)
- Data Commons (34)
- Data Sets (27)
- Machine Learning (25)
- Artificial Intelligence (25)
- Seminar Series (22)
- Leadership Updates (14)
- Imaging (13)
- Policy (10)
- High-Performance Computing (HPC) (9)
- Jobs & Fellowships (7)
- Semantics (6)
- Funding (6)
- Proteomics (5)
- Information Technology (4)
- Awards & Recognition (3)
- Publications (2)
- Request for Information (2)
- Childhood Cancer Data Initiative (1)

Leave a Reply