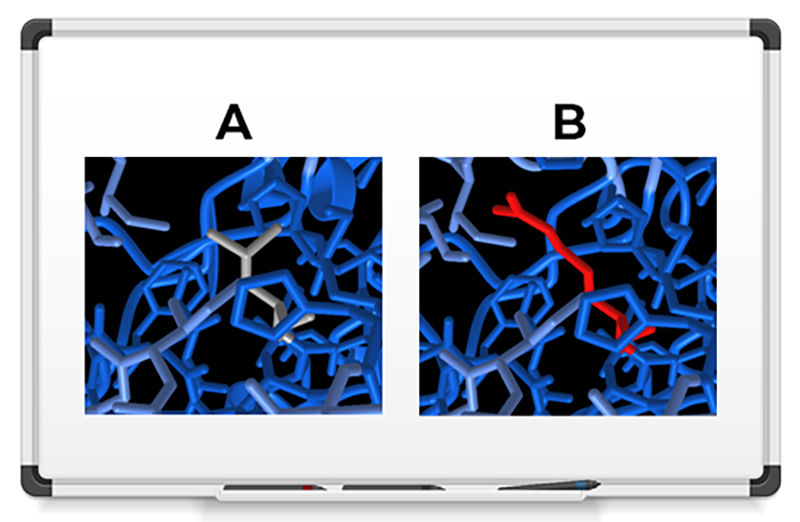
We used 3DVizSNP to sort and prioritize variants according to their 3D structural information. Using data from The Cancer Genome Atlas Program (TCGA), we filtered a list of 27,526 variants to identify mutations that were most likely to be damaging. We then fed those 901 resulting variants into the 3DVizSNP tool. We identified a mutation in a Cytochrome P450 protein (the AlphaFold2 structure prediction is shown above), which helps protect against cancer. The mutation changes a neutral leucine amino acid (A) to a charged arginine (B), and results in a destabilized version of the protein.